Welcome to www.BSCSUS.com. I have a YouTube channel called as: "@BS-CS-US". I am sharing my journey here while pursuing Bachelor-of-Science in Computer-Science - Software-Engineering option in the United-States, from Aug. 2021 onwards. I have 1 Medical degree and 2 Business degrees already. This is my 4th university degree - still ongoing.
Featured Post
What is this blog about?
ABOUT : "BSCSUS" in [ bscsus dot com ] name stands for "BS in CS in US", which stands for Bachelor of Science in Compute...
Right click image below & "open link in new tab"
Labels
- Videos - Made By Others (157)
- My Own Original Blog Posts (28)
- Information from Internet (21)
- Information from Academia (16)
- Videos - Made By Me (13)
- Website Recommendation (3)
- Book Recommendation (2)
Search This Blog
Thursday, December 23, 2021
Thursday, September 30, 2021
Monday, September 27, 2021
What is a Programming Language? History, Basics, Intro etc. from a few sources...
INTRODUCTION
Check out this awesome video from Study.com at this link:
From the link of Codecademy:
“Put simply, programming is giving a set of instructions to a computer to execute. If you’ve ever cooked using a recipe before, you can think of yourself as the computer and the recipe’s author as a programmer. The recipe author provides you with a set of instructions which you read and then follow. The more complex the instructions, the more complex the result!”Programming languages are the tools we use to write instructions for computers to follow.
Low-Level vs. High-Level Programming Languages
Programming languages fall into two different classifications - Low-level and High-level.
Low-level programming languages are closer to machine code, or binary. Therefore, they’re more difficult for humans to read (although they’re still easier to understand than 1s and 0s). The benefit of low-level languages is that they’re fast and offer precise control over how the computer will function.
High-level programming languages are closer to how humans communicate. High-level languages use words (like object, order, run, class, request, etc.) that are closer to the words we use in our everyday lives. This means they’re easier to program in than low-level programming languages, although they do take more time to translate into machine code for the computer.
As computers have become more powerful, the difference in runtime between low-level and high-level programming languages is often only milliseconds. As a result, high-level languages do the trick in most scenarios.
Most popular programming languages
There are tons of programming languages out there that allow you to do all sorts of things, from building virtual reality experiences to creating video games and more. There’s even a programming language that consists entirely of emojis!
In this section, we’ll break down some of the most popular programming languages — and what they’re used for. GitHub’s PYPL Index ranks programming languages according to how often tutorials are searched on Google.
Python: Python is a versatile, general-purpose programming language. It can be used in a variety of fields from data science and machine learning to web development and is a great first language to learn.
Java: Another language that’s great when you’re starting out, Java can be used for many things, including mobile applications, software development, and large systems development. AP Computer Science is currently taught in Java.
JavaScript: JavaScript is a front-end and back-end friendly language that enables web applications, game development, and mobile applications.
C#: C#, Microsoft’s popular programming language, can be used for a wide variety of applications, including game development, enterprise software, video games, mobile apps, and more.
C++: C++ is one of the most powerful programming languages and is used in a wide range of industries, including VR, software and game development, robotics, and scientific computing.
PHP: PHP is a widely-used server-side language. It’s a great choice if you’re interested in building dynamic web applications and works well with databases and HTML.
R: R is a statistical programming language that’s popular among data scientists. It’s used for answering questions with data analysis and creating data visualizations..
Swift: Swift is Apple’s programming language and is a must if you plan to develop applications for iOS and MacOS.
Kotlin: Kotlin is an open-source programming language developed by JetBrains. It’s popular for web development, Android development, and more.
From the link:
Most programming languages consist of instructions for computers. There are programmable machines that use a set of specific instructions, rather than general programming languages.
The description of a programming language is usually split into the two components of syntax (form) and semantics (meaning).
Programming language theory is a subfield of computer science that deals with the design, implementation, analysis, characterization, and classification of programming languages.
- The first major languages and
- The second major languages, which are in use today.
In 1945, John Von Neumann was working at the Institute for Advanced Study. He developed two important concepts that directly affected the path of computer programming languages.
(2) The second concept was also extremely important to the development of programming languages. Von Neumann called it “conditional control transfer” (www.softlord.com). This idea gave rise to the notion of subroutines, or small blocks of code that could be jumped to in any order, instead of a single set of chronologically ordered steps for the computer to take. The second part of the idea stated that computer code should be able to branch based on logical statements such as IF (expression) THEN, and looped such as with a FOR statement. “Conditional control transfer” gave rise to the idea of “libraries,” which are blocks of code that can be reused over and over.
In 1949, a few years after Von Neumann’s work, the language Short Code appeared (www.byte.com). It was the first computer language for electronic devices and it required the programmer to change its statements into 0’s and 1’s by hand. Still, it was the first step towards the complex languages of today.
In 1957, the first of the major languages appeared in the form of FORTRAN. Its name stands for FORmula TRANslating system. The language was designed at IBM for scientific computing. The components were very simple, and provided the programmer with low-level access to the computers innards. Today, this language would be considered restrictive as it only included IF, DO, and GOTO statements, but at the time, these commands were a big step forward. The basic types of data in use today got their start in FORTRAN, these included logical variables (TRUE or FALSE), and integer, real, and double-precision numbers.
Though FORTAN was good at handling numbers, it was not so good at handling input and output, which mattered most to business computing.
In 1958, John McCarthy of MIT created the LISt Processing (or LISP) language. It was designed for Artificial Intelligence (AI) research. Because it was designed for a specialized field, the original release of LISP had a unique syntax: essentially none. Programmers wrote code in parse trees, which are usually a compiler-generated intermediary between higher syntax (such as in C or Java) and lower-level code. Another obvious difference between this language (in original form) and other languages is that the basic and only type of data is the list; in the mid-1960’s, LISP acquired other data types. A LISP list is denoted by a sequence of items enclosed by parentheses.
Pascal was begun in 1968 by Niklaus Wirth. Its development was mainly out of necessity for a good teaching tool. In the beginning, the language designers had no hopes for it to enjoy widespread adoption. Instead, they concentrated on developing good tools for teaching such as a debugger and editing system and support for common early microprocessor machines which were in use in teaching institutions.
Pascal was designed in a very orderly approach, it combined many of the best features of the languages in use at the time, COBOL, FORTRAN, and ALGOL.
C Language was developed in 1972 by Dennis Ritchie while working at Bell Labs in New Jersey.
Ritchie developed C for the new Unix system being created at the same time. Because of this, C and Unix go hand in hand.
In the late 1970’s and early 1980’s, a new programing method was being developed. It was known as Object Oriented Programming, or OOP.
C++ was designed to organize the raw power of C using OOP, but maintain the speed of C and be able to run on many different types of computers.
In the early 1990’s, interactive TV was the technology of the future.
Though Java has very lofty goals and is a text-book example of a good language, it may be the “language that wasn’t.”
Visual Basic is often taught as a first programming language today as it is based on the BASIC language developed in 1964 by John Kemeny and Thomas Kurtz.
Microsoft has extended BASIC in its Visual Basic (VB) product.
Perl has often been described as the “duct tape of the Internet,” because it is most often used as the engine for a web interface or in scripts that modify configuration files. It has very strong text matching functions which make it ideal for these tasks. Perl was developed by Larry Wall in 1987 because the Unix sed and awk tools (used for text manipulation) were no longer strong enough to support his needs. Depending on whom you ask, Perl stands for Practical Extraction and Reporting Language or Pathologically Eclectic Rubbish Lister.
Programming languages have been under development for years and will remain so for many years to come.
- They got their start with a list of steps to wire a computer to perform a task.
- These steps eventually found their way into software and began to acquire newer and better features.
- The first major languages were characterized by the simple fact that they were intended for one purpose and one purpose only,
- However, the languages of today are differentiated by the way they are programmed in, as they can be used for almost any purpose.
The basic components of a computer are:
- Input unit
- Central Processing Unit(CPU)
- Output unit
- Memory unit
- Control unit
- Arithmetic Logic unit
- Software is a set of programs that performs multiple tasks together.
- An operating system is also software (system software) that helps humans to interact with the computer system
The piece of code given below performs a basic task of printing “hello world! I am learning programming” on the console screen. We must know that keyboard, scanner, mouse, microphone, etc are various examples of input devices, and monitor(console screen), printer, speaker, etc are examples of output devices.
Between high-level language and machine language, there are assembly languages also called symbolic machine code.
Characteristics of a programming Language:
- A programming language must be simple, easy to learn and use, have good readability, and be human recognizable
- Abstraction is a must-have Characteristics for a programming language in which the ability to define the complex structure and then its degree of usability comes
- A portable programming language is always preferred
- Programming language’s efficiency must be high so that it can be easily converted into a machine code and executed consumes little space in memory
- A programming language should be well structured and documented so that it is suitable for application development
- Necessary tools for the development, debugging, testing, maintenance of a program must be provided by a programming language
- A programming language should provide a single environment known as Integrated Development Environment(IDE)
- A programming language must be consistent in terms of syntax and semantics
- C
- Python
- C++
- Java
- SCALA
- C#
- R
- Ruby
- Go
- Swift
- JavaScript
- C
- Python
- C++
- C#
- R
- Ruby
- COBOL
- ADA
- Java
- Fortran
- BASIC
- Altair BASIC
- True BASIC
- Visual BASIC
- GW BASIC
- QBASIC
- PureBASIC
- PASCAL
- Turbo Pascal
- GO
- ALGOL
- LISP
- SCALA
- Swift
- Rust
- Prolog
- Reia
- Racket
- Scheme
- Shimula
- Perl
- PHP
- Java Script
- CoffeeScript
- VisualFoxPro
- Babel
- Logo
- Lua
- Smalltalk
- Matlab F F#
- Dart
- Datalog
- dbase
- Haskell
- dylan
- Julia
- ksh
- metro
- Mumps
- Nim
- OCaml
- pick
- TCL
- D
- CPL
- Curry
- ActionScript
- Erlang
- Clojure
- DarkBASCIC
- Assembly
- HIGH-LEVEL LANGUAGE -->
- ASSEMBLEY LANGUAGE -->
- MACHINE LANGUAGE -->
- COMPUTER HARDWARE
Sunday, September 26, 2021
Friday, September 24, 2021
Practice Coding on ProgramIZ.com and Edabit.com
It helps to practice coding as much as possible. That is the best way to learn.
I have used ProgramIZ.com already, as below.
Another website that one I came across is Edabit.com as below.
Created a GitHub account ! Handle: @50mj
Am slowly trying to become a part of the Computer Science community! Just joined GitHub, and created an account with the handle "@50mj". Hope to get more familiar and make good progress soon! I am impressed by the initial feel and experience of the site. It is probably one of the best websites I have ever visited, in terms of visuals and graphics! I think you should try it too!
C++ About, Resources, Pros & Cons
Link to the C++ Foundation Website: www.ISOCPP.org
Information below is from this link and this link:
- C++ (pronounced "see plus plus") is a computer programming language based on C. It was created for writing programs for many different purposes. In the 1990s, C++ became one of the most used programming languages in the world
- The C++ programming language was developed by Bjarne Stroustrup at Bell Labs in the 1980s, and was originally named "C with classes". The language was planned as an improvement on the C programming language, adding features based on object-oriented programming. Step by step, a lot of advanced features were added to the language, like operator overloading, exception handling and templates
- C++ runs on a variety of platforms, such as Windows, Mac OS, and the various versions of UNIX
- C++ is a general-purpose programing language which means that it can be used to create different variety of applications
- C++ is used for variety of application domains
C++ was designed with an orientation toward system programming and embedded, resource-constrained software and large systems, with performance, efficiency, and flexibility of use as its design highlights.
Why should you learn C++?
The C++ language originally derives from the imperative language C. The defining feature which distinguishes C++ from C is support for Object-Oriented Programming (OOP). This makes C++ a multi-paradigm programming language. An example that can help to demonstrate what OOP means:
If you were writing a program to track the statistics of a racing cyclist, you might make different parts of the program for their age, years of racing, wins, falls, what teams they've raced with and so on. In real life, though, that's not how we think. Instead, we would think of the cyclist as a whole, and the different statistics as being part of him. We could also apply that general "model" of a cyclist, maybe with a few modifications, to any cyclist, and have a complete representation of them. This is the essence of object-oriented programming, and as you understand it more fully, it will allow you to create powerful, yet easily-understood programs. Instead of relying on data that is scattered throughout a program, you can create a block of code that defines everything you need, and then reuse that throughout the program.
EXAMPLE: Think of a motor car. You unlock it with the key and get in. Then, you turn the ignition, put the car in reverse, release the brake, and press the accelerator. As you drive, you use the steering wheel, the brake, and the accelerator (and maybe the clutch). You don't know or need to know all the specifics of the car to make it work. You just use what you need, and it's simple, too. Object-oriented programming is like that. You can make powerful code, but it's all hidden, and you can interact and reuse that code using simple controls.
Other languages, such as Java, Python, Smalltalk and C#, allow the programmer to write code in this object-orientated way. The key difference between C++ and these languages is that C++ is designed to be compiled into efficient low-level code which can run directly on the processor of a computer. This ability means that C++ differs in many ways from these other languages, and lacks many of the advanced facilities you might be familiar with if you already know one of them.
Pros and Cons of C++
PROS:
- Is extremely popular, and therefore lots of support is available
- Has a large base of freely available code for download, while also supporting direct integration with ASM and C
- Is very powerful, and can be used to create just about any program, including low-level system programs
- There is a compiler for C++ on every major operating system. C++ programs that are purposely written for portability will work on many major operating systems with little change in code
- C++ is a language which is compiled (transformed from human readable code to low-level machine code), so it can often run faster than languages such as Java, Python, and C#, as it does not depend on an interpreter or a "run-time environment" which must be loaded beforehand
- Has a long-established usage base that likely guarantees support for the language will continue for quite some time
- Many languages are based off of C/C++, such as Java, so knowledge in C++ will make it easier to understand these languages
- Has a relatively small associated C++ Standard Library as compared to languages such as Java's Standard Platform SDK or C#'s .NET Framework, permitting greater versatility and reducing the system footprint of resulting compilations
- Has been standardized by the International Standards Association as ISO/IEC 14882 with significant versions of the standard released in 1998, 2003 and 2011
- Has a significant number of open source libraries available, including the Boost which are freely and widely available
- It is not very safe by itself, as it lacks automatic boundary checks, invalid pointer checks, etc., allows for invisible side-effects (causing non-deterministic behavior) and allows implicit type casting. Many security issues and memory leaks are a direct result of this, unless an extra effort is made to prevent them
- By default, there is no built-in memory management, even if smart pointers introduced from C++11 allow automatic resource managment
- Its OOP system is rather archaic, requiring explicit virtualization of methods among other things usually reserved for older languages
- Lacks the ability to define completely custom operators. (Not to be confused with the ability to define custom implementations for a hard-wired set of operators, which C++ has.)
- Does not offer full algebraic data types
- Functions are not first-class types. (Although pointers allow for workarounds.)
- Has a somewhat more difficult learning curve than some other languages. For instance, C++'s most powerful features, such as templates, have a very complex syntax
- Is very picky how code is formatted (but not quite as picky as FORTRAN, RPG or Haskell). For example, if you forget to add a semicolon, the program won't compile.
- GUI, Networking aren't standardized, requiring the use of non-standard, third-party libraries (though many such libraries, both free and commercial, are available, as is the possibility to use C libraries), Boost being one of the preferred. The lack of a standard, however, may hamper learnability and interoperability or at least require some extended investigation
MOOC = Massive Open Online Course(s)
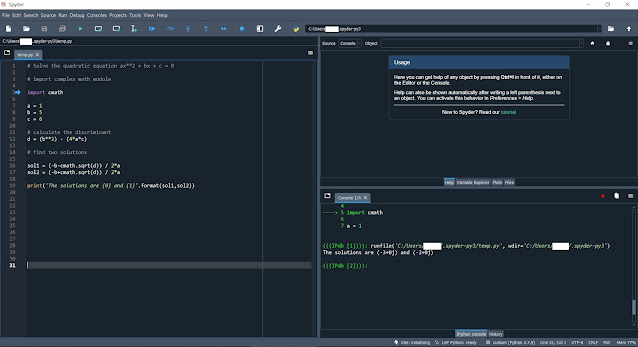
Sample Python Program on Spyder IDE. Made by me today !
Today, it has been just 1 month since I started the program, BS in CS in the US on 23 August, 2021. And it has been just 2 months since I decided to enroll into the program on 23 July, 2021 and started this blog. Below is a sample python program after just 1 month of starting the program ! This was written by me after referring to an example on the internet at this link.
No, I am not yet able to write code on my own, from memory. Yes, I do have to look at examples and look up commands on the internet or from the text book. No, I am not perfect yet.
HOWEVER, I am now able to get some work done! I am able to solve problems and create solutions using software now! Since I have the basic knowledge and basic tools now, I can build on that to achieve better and higher results!
Right now, I am only doing Python and C++ as well as NI Multisim circuit drawings. However, I am happy that my work is relatively clean and bug free for now!
Cheers,
Jerry
Thursday, September 23, 2021
Software Development: About, Process, Activities
From the link:
"ABOUT:
- Software development is the process of creating a computer software
- It includes the software release life cycle of preparing a design, coding the program, and fixing the bugs. The final goal is software release of a product that serves the wishes of users
- Software product is usually a result of research, new development, prototyping, modification, reuse, re-engineering, maintenance, or any other activities
A software development process (model, methodology) is a system that is used to structure, plan, and control the process of developing information systems. Each model is defferent, more or less structured and is considered to be suitable to only some kinds of projects.[3]
There are several stages of software development:
Analyzing the problem
- Market research
- Gathering requirements for the proposed software
- Devising a plan or design for the software
- Implementation (coding) of the software
- Testing the software
- Deployment
- Maintenance and bug fixing
- Understanding the need: There are different sources of ideas for software products like market research. The next step is market evaluation. It includes a check of cost and time assumptions, economic feasibility, fit with existing channels distribution, effects on existing product lines, required features, fit with the company's marketing objectives. This process is also connected with non-technical activities like human resources, risk management, intellectual property, budgeting, crisis management, etc.
- Planning: An important task in creating a software program is understanding the requirements. The software engineers must accept the client's idea and adapt it to the working process.
- Designing: After establishing the requirements, the engineers start creating a software design document. Design of the software means the high-level design of the main modules with a full picture of how the parts fit together. The language, operating system, and hardware components should be clear at this stage.
- Implementation, testing and documenting. There are 3 next processes which are combined: (1) Implementation - programming the code for the project (2) Testing - looking for defects (3) Documenting - making documents of the inner design of software, API can be also included
- Deployment and maintenance: The deployment includes installation, customization, testing, and possibly a longer period of evaluation. Software training and support are important because software is only effective if it is used rightly. Maintaining and improving software is the stage to cope with new faults or requirements, it usually takes a lot of time and effort"
Software Engineering: About, Steps, Tools
From the link:
"ABOUT:Software engineering is a field of engineering, for designing and writing programs for computers or other electronic devices. A software engineer, or programmer, writes software and compiles the software to make instructions that the computer can follow.
Good quality software is easier to fix and add new features. Good documentation and good design are parts of good software.
- Getting the requirements
- Planning
- Writing
- Documenting
- Testing the software
- Release
STEPS in creating software: Software engineering can broadly be split into the following steps:
- Requirements say what the software should do.
- Software design is usually done on paper. It says what the different parts of the software are, and how they talk to each other.
- After the design phase is done, each component (part) of the software is coded. Code is what tells the computer exactly what to do at each step.
- Testing is done to see if the components meet the requirements and that the system as a whole meet the requirements.
- Part or all of this process can be repeated if software bugs are found or new requirements are needed
- Flowcharts
- UML diagram
- Debugging tools
- Compiler
- Text editor, usually part of an IDE - Integrated Development Environment
- Database"
Computer Science
From the link:
"Computer science deals with the theoretical foundations of information, algorithms and the architectures of its computation as well as practical techniques for their application.- Computer Science is the study of algorithmic processes, computational machines and computation itself. As a discipline, computer science spans a range of topics from theoretical studies of algorithms, computation and information to the practical issues of implementing computational systems in hardware and software.
- Its fields can be divided into: (1) Theoretical and (2) Practical disciplines.
- The theory of computation concerns abstract models of computation and general classes of problems that can be solved using them
- Computer Graphics or Computational Geometry emphasize more specific applications
- Algorithms and data structures have been called the heart of computer science
- Programming language theory considers approaches to the description of computational processes, while computer programming involves the use of them to create complex systems
- Computer architecture describes construction of computer components and computer-operated equipment
- Artificial intelligence aims to synthesize goal-orientated processes such as problem-solving, decision-making, environmental adaptation, planning and learning found in humans and animals"
Programmer / Coder / Software Developer
From the link:
"A computer programmer is a person who makes computer programs using a programming language. Programmers are also called software developers, coders, or hackers. A programmer's main jobs are writing program source code, testing if it works, and debugging (fixing) the program if there are problems. Programmers often use software tools such as text editors and IDEs (Integrated Development Environments) to help them work. Computer programming is a profession that can be done from a computer anywhere in the world. This is called telecommuting - doing work on the Internet instead of in an office. Some programmers are famous because their software is used by many people. One example is Linus Torvalds, who created an important part of the Linux operating system. Programming can be done in many different languages and can look very different but do the same thing. An example of this is the Hello world program"Computer Programming - Some terms
From the link:
"Programming: Computer programming is the process of telling a computer to do certain things by giving it instructions. These instructions are called programs. A person who writes instructions is a computer programmer. The instructions come in different languages; they are called programming languages. There are many programming languages. Sometimes, programmers use special software, such as integrated development environments (IDEs), which have many special parts, including a text editor, to help them to type and edit programs.
Computers understand instructions directly if those instructions are written in machine code, special characters that can be processed by the computer but are difficult for humans to read. Writing these instructions directly in machine code takes a long time and is difficult, so instructions are written in a language easier for people to use, which the computer converts into "computer form" instructions (in other words, machine code) so the computer can follow them. The simplest of these is assembly language. Programs written in a language more like English are converted by a compiler. Some languages, called interpreted languages, use interpreters instead of assemblers or compilers.
Once a program has been compiled the instructions in it are written into a file that contains a series of numbers that the computer can understand. These machine-instructions will be loaded into the memory computer's so that the can run them when the executable is opened.
Variables: A variable is a piece of the program that can be changed. Variables can include information added by the user, or answers that are found as a result of a calculation.
Conditionals: Conditionals are parts of the program that work if something the program can check to see whether it is true. If that part is not true, then the program won't make it happen. A conditional is often done with an "If Statement". Some words used are: "if", "else", "else if",
Comments: In the program, a comment is information that is meant to be read by people who are reading the program. Comments have a special symbol in front of them that tells the computer that they are comments and should not be read as code. Comments are used to explain how a certain part of a program works. This is helpful when multiple people are working on the same program, and if they need to work on a section where someone else was working on. If the programmer that was working on it first left behind comments for any other programmer that works on it later, it will help them know faster what is going on in the program.
Debugging: Computer programmers make mistakes when writing codes. The mistakes are called bugs and cause the program to follow the wrong instructions. Debugging is the process of finding and fixing the mistakes. To debug code is to find such mistakes. There are many debugging methods. Software such as text editors and IDEs have tools that can detect specific mistakes in the codes before the program is executed. Programmers can also use programs called debuggers. A debugger can run a program step by step and track how values of specific variables change when the program is running. Programmers can use a debugger to find where the mistake happened in the code
IDE (Integrated Development Environment): It is a computer program that makes it easier to write other computer programs. They are used by computer programmers to edit source code, and can be easier to use than other text editors for new programmers. They can have compilers so programmers don't have to open other programs to compile the source code. They also often have syntax highlighting. A feature of an IDE is to check the syntax, and libraries can be added to increase functionality. It also may have predictive coding that can finish lines with syntax such as brackets or semicolons and can suggest variables to be used. It also may have debuggers that can step through lines, take breaks and inspect variables. An IDE often comes with an interpreter and a compiler. Certain IDEs can allow multi-language which means that functions can be written in different languages"
Compiler
From the link:
"A compiler is a computer program that translates computer code written in one programming language into another programming language.
- The first language is called the source language, and the code is called SOURCE CODE.
- The second language is called the target and can usually be understood by computers. In that case, the instructions become MACHINE CODE.
A compiler usually has 3 STEPS:
- It reads the text and makes notes about how the instructions go together. If the instructions don't make sense, it will try to tell the programmer
- Then it will use what it knows about the target language to make the instructions fit better
- It then writes down the instructions in the target language. If the source instructions are on different pages, it may have to compile several before it can write everything down"
About Programming Language (source: Wiki)
From the link:
"A programming language is a type of written language that tells computers what to do.A programmer writes text in the source code of a programming language to make programs. Usually, the programming language uses real words for some of the commands (e.g. "if... then... else...", "and", "or"), so that the language is easier for a human to understand. Like any normal language, many programming languages use punctuation. Many programs are then compiled, which means that the computer changes, or translates, the source code into another language (such as assembly language or machine language) that a computer can read, but which is much harder for a person to read"
Types of Programming Language:
- High-level vs. Low-level
- Declarative vs. Imperative programming
- Functional vs. Procedural
- Stack based
- Object-Oriented
- Flow-Oriented
- Scientific-Computing
- Document Creation
Saturday, September 18, 2021
What is Mechatronics? More than simply "Mechanics" + "Electronics"...
From the link:
"Many people treat mechatronics as a modern buzzword synonymous with Automation, Robotics and Electromechanical Engineering.
Mechatronics, also called Mechatronics Engineering, is an interdisciplinary branch of engineering that focuses on the integration of Mechanical, Electronic and Electrical Engineering systems. Also includes a combination of Robotics, Electronics, Computer Science, Telecommunications, Systems, Control, and Product Engineering.
As technology advances over time, various subfields of engineering have succeeded in both adapting and multiplying. The intention of mechatronics is to produce a design solution that unifies each of these various subfields. Originally, the field of mechatronics was intended to be nothing more than a combination of mechanics and electronics, hence the name being a portmanteau of mechanics and electronics; however, as the complexity of technical systems continued to evolve, the definition had been broadened to include more technical areas."
From the link:
"Mechatronics is a multidisciplinary field that refers to the skill sets needed in the contemporary, advanced automated manufacturing industry. At the intersection of Mechanics, Electronics, and Computing, Mechatronics specialists create simpler, smarter systems. Mechatronics is an essential foundation for the expected growth in automation and manufacturing.
Mechatronics deals with Robotics, Control Systems, and Electro-Mechanical systems. If you like Mechanics, Robotics, or Production equipment, have a knack for creative problem solving, enjoy technical and engineering activities, Mechatronics could be for you.
Mechatronics specialists can perform across multiple disciplines and have a solid base from which to grow. Mechatronics specialists know both mechanical and electrical engineering fundamentals - they speak both languages - so a mechatronics specialist can work with both mechanical and engineering teams.
Mechatronics specialists work with massive industrial robots, smaller robots in pick-and-place operations, control systems for bottling or packaging of food and drink products, drones, designing control systems for rides in amusement parks, prototype development.
Some mechatronics specialists are employed in firms where it is necessary to design and maintain automatic equipment. This includes industries such as manufacturing, mining, aviation, robotics, defense, and transport. Other mechatronic specialists are employed by large manufacturing companies involved in high-volume production. Many new career opportunities are on the horizon due to technological advances".
From the link:
"Mechatronics involves a combination of Mechanical and Electronic skills. It is becoming widely adopted in advanced manufacturing operations because it covers a wide array of specialties. Companies are very interested in hiring people who have the knowledge to keep their lines running at full capacity, with as little down-time as possible.
Mechatronics professionals work with Hydraulics, Pneumatics, Robotics, Automated Controls, Programmable Controllers, Process Control and Mechanical applications. They can also design, implement, manufacture, service and repair a wide array of equipment for their employers.
What does that mean in simple English, in layman's terms?
In manufacturing, time lost is money lost. If a part breaks down, the production stops and the company loses money. Every moment that a piece of equipment is down can mean big losses. It can be really expensive to replace a piece of machinery just because a few parts stop working.
Companies look to hire technicians who can identify and solve problems before they cause outages. In the worst case scenario, they need people who can quickly repair machinery if it goes down.
Companies prefer to hire technicians who have the skills to repair the whole system, ideally speaking - including robotics, electrical and mechanical systems.
Mechatronics technicians have the skills and the know-how to repair any of those systems.
Since they are knowledgeable in so many areas, the Mechatronics technician is in high demand in a large variety of industries - Aerospace, Robotics, Automotive Production, Manufacturing and even Business. As manufacturing continues to become even more advanced, the future of Mechatronics looks very bright"
Hardware Notes: For my self-learning and subject revision
- Digital technology - is everywhere in our lives
- It is important to have a good foundation in fundamentals of Digital Technology
- It is important to know Programmable Logic
- "Digital": The word is used because work happens by counting digits
- Digital Technology has progressed from: Vacuum-Tube --> Circuits --> Discrete Transistors --> complex ICs (Integrated Circuits)
- Many integrated circuits contain millions of transistors
- Many transistors are programmable
- Electronic circuits: 2 categories: (1) Digital and (2) Analog
- Still typing, while learning...
Friday, September 17, 2021
Tuesday, September 14, 2021
UNIX Operating System
(From Wikipedia at the link)
"Unix (trademarked as UNIX) is a family of multitasking, multiuser computer operating systems "
This is just an initial post. More information coming soon...
Monday, September 13, 2021
Main topics in the book: Coding all-in-one for Dummies
- What is coding?
- Programming for the web'
- Becoming a programmer
- Exploring coding career paths
- Exploring undergraduate and graduate degrees
- Training on the job
- Coding career myths
- Exploring basic HTML
- Getting more of HTML
- Getting stylish with CSS
Building floating page layouts - Using alternative positioning
- Working faster with Twitter bootstrap
- Adding in JavaScript
- Understanding Callbacks and Closures
- Embracing AJAX and JSON
- jQuery
- Building your own App
- Researching your first web application
- Coding and debugging your first web application
- Wrapping your head around Python
- Installing a Python distribution
- Working with real data
- Conditioning data
- Shaping data
- Crash course for MatPlotLib
- Visualizing data
- Exploring Data Analysis
- Exploring four simple and effective algorithms
- How to machines learn?
- Demystifying the Math behind Machine Learning
- Descending the right curve
- Validating Machine Learning
- Starting with Simple learners
- Leveraging similarity
- Hitting complexity with Neural Networks
- Resorting to ensembles of learners
- Real world applications
Main and Subtopics in the Middle School Study Guide book
(These topics are from the CS & Coding book as below)
Computing Systems
- What is Computer Science?
- What is a computer?
- How do we interact with computers?
Data and Analysis
- Storing information
- Collecting and using information
Software Engineering
- Designing computer systems
- Testing
- Documenting
- Incorporating feedback
- Collaborating
Algorithms and Programming
- Using algorithms
- Programming languages
- Computational thinking
Universal Programming Principles
- Variables
- Conditional statements
- Loops
- Events
- Procedures
Programming with Scratch
- Start
- Basic algorithms
- Data and Operators
- Control Blocks and Event Blocks
- Reusing Scripts
Programming in Python
- Start
- Variables
- Strings
- Numbers as variables
- Lists and Boolean expressions
- For loops
- While loops
- Nested loops
- Conditional statements
- Functions
Web Development
- What is the internet?
- Cybersecurity
- Creating a basic webpage
- HTML text elements
- Link elements
- Styling with CSS
- Styling individual elements with CSS
CS50 2020 - Lecture 0 - Scratch | Basics of CS
- Introduction
- Representation
- Binary
- ASCII
- Unicode
- RGB
- Algorithms
- Finding David
- Solving Problems Efficiently
- Pseudocode
- Scratch
- Hello, World
- Variables
- Text to Speech
- Sounds
- Loops
- Pen
- Conditions
- Variables
- Animation
- Sensing
- Video Motion
- Broadcasts
- Translation
- Custom Blocks
- Gingerbread Tale
- Oscartime
- Raining Men
Sunday, September 12, 2021
Good Online Learning Websites for Computer Science in Sep. 2021
From the link and online search.
Also check out this useful article "The 15 best free or affordable online computer science courses, including options from Harvard, MIT, and Stanford" at this link.
The following are 11 good websites to learn about Computer Science and other topics:
- GitHub.com at link
- Udemy.com
- KhanAcademy.org
- Coursera.org
- SkillShare.com
- Brilliant.Org
- Udacity.com
- Lynda.com
- MasterClass.com
- PluralSight.com
- Codecademy.com
- edX.org
- Alison.com
- LinkedIn Learning
- TeachYourselfCS.com
- ComputerScience.org
- OpenCulture.com
- ClassCentral.com
- FreeCodeCamp.org
- Harvard.edu - Online Computer Science Courses
- HackReactor.com
- FlatIronSchool.com
- CodingDojo.com
- AppAcademy.io
- My GreatLearning.com
- TeamTreeHouse.com
- Thinkful.com
- Practicum.Yandex.com
- FullStackAcademy.com
- DevCodeCamp.com
- GeneralAssemb.ly (Bit Maker)
- BrainStation.io
- TheDataIncubator.com
- Galvanize.com
- HolbertonSchool.com and Holberton.us
- SpringBoard.com
- North Western Bootcamps
- MIT xPro
- LambdaSchool.com
- DevMountain.com
- CS50 channel on YouTube at link
- MIT OpenCourseWare channel on YouTube at link
- TheNewBoston channel on YouTube at link and so on...
American Unicorn StartUp Companies in 2021
List of American companies that are worth over a billion dollars, as of Sep. 2021, in no particular order, from the link.
Remember, this a list of companies, not just Apps. Also remember that only some companies, and only American companies are listed here!
- SpaceX - Aerospace
- Instacart - Retail
- Epic Games - Video games
- Databricks - Software US
- Rivian - Automotive
- Chime - Financial services
- Fanatics - E-commerce
- GoPuff - E-commerce
- Plaid - Financial Technology
- Biosplice Therapeutics - Health
- Aurora - Self-driving cars
- Figma - Software
- Gusto - Software
- Reddit - Internet media
- Ripple - Computer software
- ServiceTitan - Software
- Tanium - Technology
- Tempus - Health
- Toast - Point of sale
- Netskope - Computer security
- Brex - Finance
- Carta - Software
- Scale AI - Artificial intelligence
- Argo AI - Artificial intelligence
- Gong - Artificial intelligence
- Discord - Software
- WeWork - Commercial real estate
- Automation Anywhere - Robotic process automation
- DataRobot - Artificial intelligence
- Better.com - Financial services
- GitLab - Software
- Thrasio -
- Airtable - Collaborative software
- Vice Media - Mass media
- Samsara - Technology
- CloudKitchens - Ghost kitchen
- JUUL Labs - Electronic Cigarettes
- Anduril Industries -
- Confluent -
- Magic Leap - Augmented Reality
- Zenefits - Human resource management
- Chainalysis - Blockchain
- Relativity Space - Aerospace
- Ginkgo Bioworks - Biotechnology
- Next Insurance - Insurance
- TripActions - Corporate Travel Management
- Niantic - Video games
- VAST Data -
- Rubrik - Computer storage
- SentinelOne -
- Automattic - Internet
- Lucid Software - Software
- Warby Parker - Retail
- Workrise - Workforce management
- Bird - Transportation
- Convoy - Trucking
- AmWINS Group -
- Mozido - E-commerce
- Houzz - Interior design
- KeepTruckin - Logistics
- Acorns - Financial technology
- Eightfold.ai - Artificial intelligence
- Nextdoor - Social network
- Udemy -
- Avant - Consumer Finance
- Intarcia Therapeutics - Pharmaceutical
- ThoughtSpot - Analytics
- Prosper Marketplace - Financial Technology
- NantOmics - Biotechnology
- Quora - Social Network
- Zocdoc - Healthcare
- dutchie - Cannabis
- PAX Labs - Cannabis
- Thumbtack
- Workato - Technology
- Afiniti - Software development
- Seismic Software
- HeartFlow -
- Duolingo - Education
- ID.me - Identity verification service
- Podium - Software
- M1 Finance - Financial technology
- Away - Retail
- NetDocuments - Software
- QOMPLX, Inc. - Computer Security
- Stash - Financial technology
- Symphony - Software
- G2 - Technology
- Knotel -
- Applied Intuition - Software
- ezCater
- Rec Room Inc - Video games
- Alation - Software
- Fair -
- FloQast - Software
- Glossier -
- Intercom - Software
- Starburst Data - Technology
- Sysdig - Cybersecurity
- Outreach - Sales
- TuSimple -
- Virta Health - Healthcare
- Wheels Up - Private aviation
- Instabase - Software
- Age of Learning, Inc. - Education
- AppDirect -
- Arctic Wolf - Cybersecurity
- Bluecore - E-commerce
- Branch Metrics
- Calabrio - Software
- Frontline Education
- Grammarly - Software
- Grove Collaborative
- InVision -
- Locus Robotics - Robotics
- Lookout Security
- Pantheon - WebOps
- Prometheus Group -
- REEF Technology - Info. Tech. & Services
- Rent the Runway - E-commerce
- Rubicon Global - Waste management
- Shape Security -
- Sift - Digital Trust & Safety
- Sonder -
- Splashtop - Software
- StockX - E-commerce
- Tekion - Software as a Service (SaaS)
- TransparentBusiness - Technology
- Tresata -
- Turo - Car sharing
- Udacity - Education
- Vox Media -
- VTS -
- Stripe - Financial services
- Tipalti - Financial Technology
- BigID - Technology
- HoneyBook - Financial services